In today’s automated world, controlling the flow of liquids and gases with precision is essential across countless systems—whether it’s in home plumbing, irrigation networks, industrial machinery or HVAC units. One component that makes this possible, quietly and efficiently, is the solenoid valve. Though small in size, these electrically controlled valves play a big role in modern fluid management by allowing systems to start, stop or redirect flow instantly—without any manual intervention.
A solenoid valve uses an electromagnetic coil to open or close the valve when activated by an electrical signal. This makes it ideal for applications where automation, speed and reliability are critical. From turning on a sprinkler system at the right time to managing the air pressure in a factory line, these valves are trusted for their fast response and compact design.
In this article, we’ll take a closer look at what solenoid valves are, how they work, the different types available and where they’re used. Whether you’re a technician, a DIY homeowner or someone exploring fluid control systems, this guide will give you a clear and practical understanding of solenoid valves and their everyday importance.
What is a Solenoid Valve?
A solenoid valve is an electromechanical device that controls the flow of fluid or gas. It uses electricity to power a solenoid, which moves a plunger inside the valve. This movement either opens or closes the valve, regulating the flow.
The valve has two key parts:
-
The Solenoid: This is the electromagnetic coil that, when energized, creates a magnetic field.
-
The Valve Body: This part contains the flow passages and houses the moving plunger that controls the flow.
When you apply electrical power to the solenoid, the magnetic field pulls the plunger into or out of position. This opens or closes the valve, allowing or stopping the flow of fluid or gas. When you cut off the power, the solenoid deactivates and a spring or gravity returns the plunger to its default position, stopping the flow.
How Do Solenoid Valves Work?
Solenoid valves come in different designs. The main difference between them lies in whether they are normally closed (NC) or normally open (NO). Let’s look at how each type works.
1. Normally Closed (NC) Valve
This is the most common type of solenoid valve. Here’s how it works:
-
No Power: When you don’t apply power, the valve stays closed and the flow of fluid or gas is blocked.
-
Power On: When you apply power, the solenoid creates a magnetic field that pulls the plunger upwards. This opens the valve and allows fluid to flow.
-
Power Off: Once you turn off the power, the solenoid deactivates. A spring then pushes the plunger back into its default position, closing the valve and stopping the flow.
This type is ideal when you want to keep the valve closed until an electrical signal opens it.
2. Normally Open (NO) Valve
The normally open valve works the opposite way:
-
No Power: When no power is applied, the valve remains open and fluid can flow freely.
-
Power On: When you apply power, the solenoid pulls the plunger, closing the valve and stopping the flow.
-
Power Off: Once you cut off the power, the spring pushes the plunger back, reopening the valve and allowing the fluid to flow again.
This valve is useful when you want the flow to continue unless an electrical signal stops it.
3. Direct-Acting vs. Pilot-Operated Valves
There are two more types based on their operation:
-
Direct-Acting Solenoid Valves: These valves don’t rely on system pressure to open or close. They work well in low-pressure systems or for small flow rates.
-
Pilot-Operated Solenoid Valves: These valves use system pressure to help open and close the valve. They are suitable for larger systems with higher flow rates or pressures.
Key Components
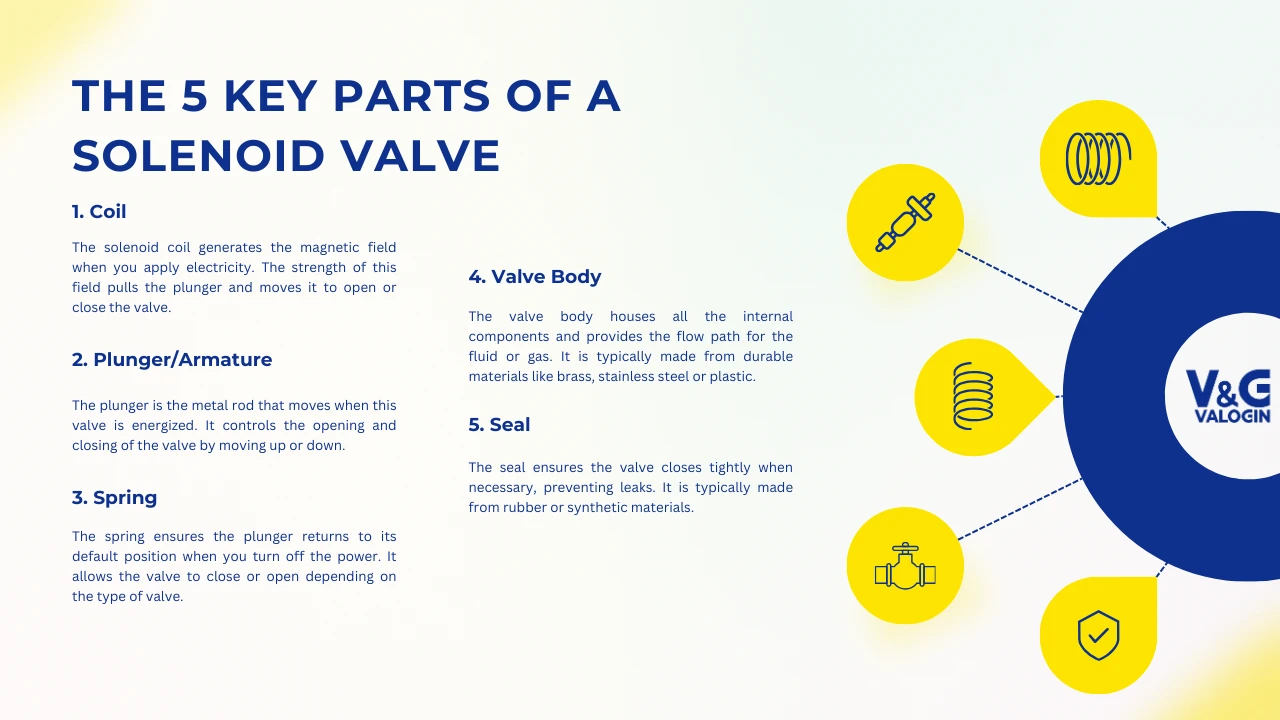
Let’s dive deeper into the key parts of a solenoid valve to understand how it works:
-
Coil: The solenoid coil generates the magnetic field when you apply electricity. The strength of this field pulls the plunger and moves it to open or close the valve.
-
Plunger/Armature: The plunger is the metal rod that moves when this valve is energized. It controls the opening and closing of the valve by moving up or down.
-
Spring: The spring ensures the plunger returns to its default position when you turn off the power. It allows the valve to close or open depending on the type of valve.
-
Valve Body: The valve body houses all the internal components and provides the flow path for the fluid or gas. It is typically made from durable materials like brass, stainless steel or plastic.
-
Seal: The seal ensures the valve closes tightly when necessary, preventing leaks. It is typically made from rubber or synthetic materials.
Each of these components plays a vital role in ensuring this valve works efficiently.
Where Are these Valves Used?
Solenoid valves have many applications across different industries. You can find them in systems that need automatic control over the flow of fluids or gases. Some of the most common uses include:
-
Plumbing Systems: These valves control water in irrigation systems, automated faucets and shut-off valves. They help manage water usage and prevent waste.
-
HVAC Systems: In heating, ventilation and air conditioning systems, these valves control refrigerants, air and water. They help maintain temperature and humidity levels.
-
Industrial Automation: In manufacturing plants, These valves control air and fluids in systems like pneumatic machines and conveyor belts. These valves make automation more efficient by reducing human involvement.
-
Medical Equipment: These valves regulate the flow of gases like oxygen and nitrous oxide in medical devices. They ensure safe and precise control over critical systems.
-
Automotive Applications: These valves control fuel, air and brake fluids in vehicles. They help manage these vital systems, ensuring smooth operation.
-
Water Treatment: In water treatment plants, These valves manage water flow during filtration and backwashing cycles, helping ensure clean water production.
Solenoid valves provide fast and reliable control in these applications, making them indispensable in modern systems.
Advantages of Solenoid Valves
Solenoid valves offer numerous advantages, making them the preferred choice for many applications. Here’s why:
-
Fast Response Time: These valves react quickly. They can open or close almost instantly, which is crucial in systems that need immediate changes in flow.
-
Remote Control: You can operate these valves remotely. This feature makes them perfect for automated systems or locations that are hard to access manually.
-
Compact Design: These valves are small, which allows them to fit into tight spaces. Their compact size makes them suitable for systems where space is limited.
-
Low Power Consumption: These valves are energy-efficient. They don’t consume a lot of power, especially when used intermittently, which helps reduce operating costs.
-
Long Service Life: These valves last longer because they have fewer moving parts than mechanical valves. This leads to lower maintenance costs.
-
Precision Control: These valves provide accurate control over fluid or gas flow, ensuring that systems work smoothly and reliably.
The combination of these benefits makes solenoid valves ideal for a wide range of industries.
Installation Tips
Correct installation ensures that your solenoid valve works properly. Follow these tips for the best results:
-
Check Voltage: Always verify that the coil voltage matches your power supply. Most solenoid valves use 12V, 24V or 110V power. Using the wrong voltage can damage the valve.
-
Match Flow Direction: Most solenoid valves have an arrow indicating the correct flow direction. Install the valve with the arrow pointing in the right direction to avoid flow issues.
-
Keep It Clean: Dust and debris can block the valve or damage internal parts. Install filters to keep the valve clean and functioning properly.
-
Use Proper Fittings: Match the valve’s inlet and outlet sizes with your pipes or tubing. This ensures a tight fit and prevents leaks.
-
Avoid Overheating: Don’t leave the solenoid powered continuously. Prolonged use can cause overheating. Use pulse controls or timers to prevent this from happening.
By following these tips, you can improve the performance and longevity of your solenoid valve.
Conclusion: Solenoid Valves for Efficient Fluid and Gas Control
Solenoid valves are essential for controlling fluid and gas flow in automated systems. They provide fast, precise and reliable performance, making them ideal for applications ranging from industrial automation to medical equipment.
These valves help save energy, reduce maintenance costs and ensure smooth operation. Understanding how solenoid valves work and installing them correctly will help you get the most out of these powerful devices.
If you have any questions or need help selecting the right solenoid valve for your system, contact us. We are here to assist with all your fluid and gas control needs.


