When you’re installing or upgrading a radiator, the type of radiator valve you choose plays a bigger role than most people realize. While radiators get the attention for heating performance and design, it’s the valves that control how hot water enters and exits—and how well the system functions. Among the first decisions you’ll need to make is whether to use straight or angled radiator valves.
At first glance, the difference seems minor. One connects in a straight line; the other makes a right-angle turn. But that small change affects installation layout, pipe routing, room space and overall appearance. Pick the wrong one, and you could end up with a messy installation, exposed pipework or a radiator that just doesn’t sit right in the room.
In this post, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know about straight and angled radiator valves. You’ll learn how each type works, when to use it and how to decide which one fits your system best. Whether you’re a DIY renovator or working with a contractor, this guide will help you get it right the first time.
What Is a Radiator Valve?
A radiator valve is a small but critical component in any hydronic (hot water) heating system. Its job is to regulate the amount of hot water flowing into the radiator. This control affects not only how much heat the radiator emits but also how efficiently the system operates as a whole.
There are two valves on most radiators. One is a flow control valve, which you turn to let more or less water in. The other is a lock shield valve, which balances the system and controls how much water exits the radiator. Together, they help ensure that every radiator in your home gets the right amount of heat.
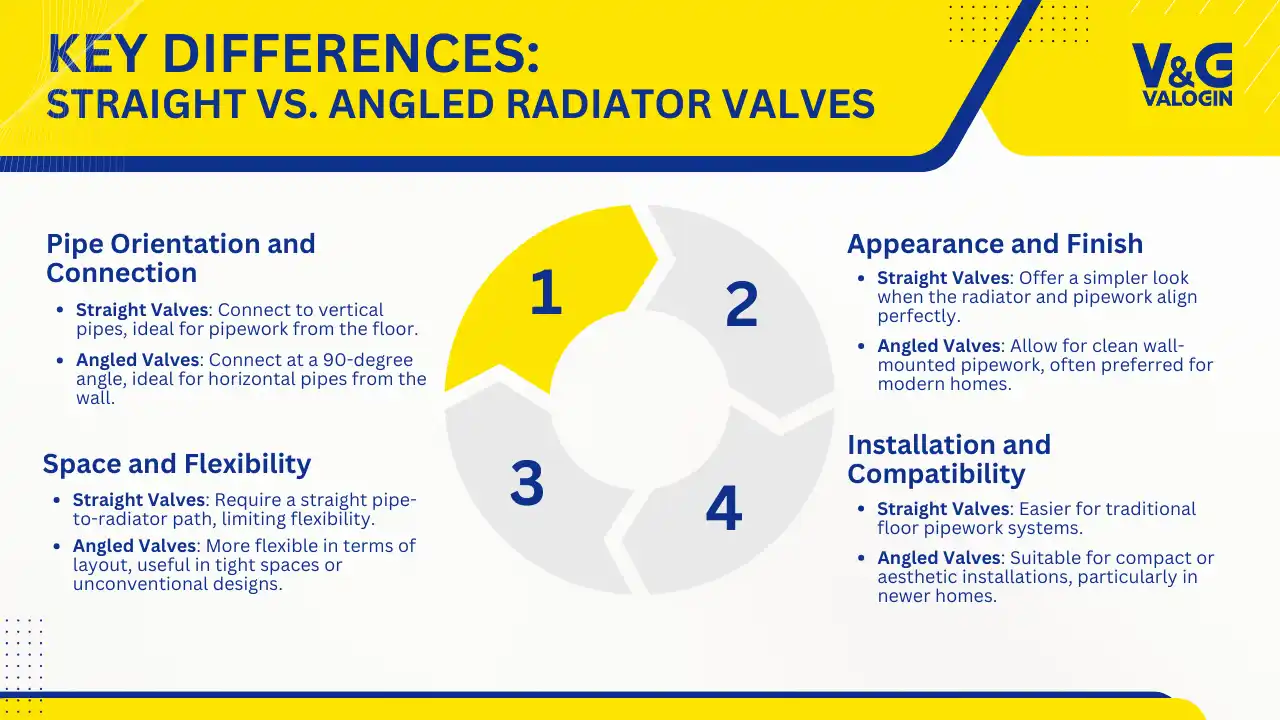
Radiator valves come in various shapes and connection styles. The two most common types are straight and angled valves. These terms refer to the orientation of the valve body and how it connects your radiator to the pipework.
What Is a Straight Radiator Valve?
A straight radiator valve has a linear design. Water enters and exits the valve in a straight path without changing direction. The pipe comes up or across in a straight line and the valve connects directly into the radiator without a bend. It’s a clean, no-turn connection from the pipe to the radiator inlet.
You’ll typically use straight valves when the pipework runs directly upward from the floor and aligns with the bottom of the radiator. This setup keeps the valve in line with the radiator’s inlet and allows water to flow upward in a smooth, uninterrupted path.
Straight valves are ideal when you have vertical pipework feeding into a radiator with bottom connections. They also work well when pipes run horizontally along the wall at the same height as the radiator’s inlet, although that’s less common. One of the key advantages of a straight valve is its clean, minimal profile. Because the pipe and valve sit in a straight line, they tend to look streamlined, especially in modern or minimalist spaces.
What Is an Angled Radiator Valve?
An angled radiator valve, as the name implies, changes the direction of the water flow by 90 degrees. Water enters the valve from one direction—typically from a pipe coming out of the wall or along the floor—and exits at a right angle into the radiator’s inlet.
This type of valve is used when the pipework doesn’t align directly with the radiator connection. For example, if your pipes run along the baseboard or come horizontally out of the wall behind the radiator, an angled valve makes it easy to turn the water up into the radiator inlet. It eliminates the need for extra fittings or visible pipe bends.
Angled valves are especially useful in older homes or tight spaces where pipe routes aren’t easily modified. They allow you to tuck the valve closer to the wall, creating a neater look and preventing the valve from protruding into the room. In smaller rooms, this space-saving design can make a noticeable difference.
They’re also the most commonly used valve type in many homes because they work in a variety of layouts and offer flexibility when dealing with complex plumbing routes.
How Straight and Angled Valves Affect Pipework
Choosing between straight and angled valves isn’t just about the valve—it’s about how the valve connects your radiator to the existing pipework. The direction your pipes approach the radiator determines which valve type makes the most sense.
If your pipes come straight up from the floor and the radiator has bottom inlets, a straight valve offers the most efficient and visually clean connection. The valve and pipe stay in line, making installation simple and reducing the need for visible elbows or bends.
On the other hand, if your pipes come from the wall behind the radiator or run along the skirting board, an angled valve allows you to connect without rerouting or modifying the pipes. It turns the flow direction neatly from horizontal to vertical (or vice versa), which is especially helpful in retrofitted systems or when installing designer radiators with specific inlet positions.
Choosing the wrong valve type can lead to awkward angles, visible pipe extensions or valves that stick out into the room unnecessarily.
Performance Differences Between Straight and Angled Valves
In terms of performance, both valve types do the same job. They control the flow of hot water into the radiator and allow the system to heat the room as intended. There’s no real difference in how much heat they allow through or how quickly a radiator warms up.
However, the orientation of the valve can impact ease of access, system aesthetics and long-term maintenance.
Straight valves are easier to work with when you have ample space and vertical pipework. They’re simple to install and access because there’s no bend or twist to manage. Angled valves, on the other hand, are better suited to tighter spaces where you need to keep things compact and unobtrusive.
Both types are available in manual and thermostatic models, so you’re not limited in terms of function—only layout.
A Note on Thermostatic and Manual Radiator Valves
Regardless of whether you’re using a straight or angled valve, you’ll also need to choose between manual and thermostatic versions. Manual valves let you open or close the flow by hand, like a tap. Thermostatic radiator valves (TRVs), on the other hand, use a built-in sensor to adjust flow automatically based on room temperature.
Both manual and thermostatic options are available in straight and angled forms. The layout of your plumbing determines which shape to use—not the function of the valve.
Just keep in mind that TRVs take up slightly more space, especially on angled valves, so make sure there’s enough clearance around the valve for the thermostatic head to sit comfortably.
What About Corner Valves?
While less common, corner radiator valves offer a third option. These valves also have a 90-degree turn, but they’re designed to connect to pipework that runs along the wall and into the side of the radiator at a matching angle. They’re often used for designer radiators or installations where exposed pipework is visible and aesthetics matter more than space savings.
Corner valves provide a visually seamless look in modern interiors but they require very specific pipework layouts and radiator inlets to function properly.
How to Choose the Right Radiator Valve
To choose the right radiator valve shape, start by looking at your pipework. The direction from which your pipes approach the radiator determines what will work—and what won’t.
If your pipes come up from the floor and your radiator has bottom inlets, you should go with straight valves. They’ll connect directly and look clean.
If your pipes come from the wall or run along the wall, you’ll want angled valves. They’ll help you turn the connection upward into the radiator without awkward bends or visible extensions.
If the radiator has side inlets and you want pipework that runs along the wall, you might need corner valves—but those are more specialized.
Also consider how much space you have, how visible the valves will be and whether you’re using manual or thermostatic controls. These small details make a big difference in the final result.
Final Thoughts: Straight vs Angled Radiator Valves
Straight and angled radiator valves both serve the same purpose: they regulate hot water entering your radiator. The difference lies in how they connect to your pipework and how they sit in your space.
Use straight valves when your pipes come up from the floor or run in a straight line with the radiator’s inlet. Use angled valves when your pipes come from the wall or require a right-angle turn to meet the radiator. Choosing the right one not only makes installation easier, it improves the look and function of your entire heating system.
It’s a small decision, but it shapes the efficiency and finish of your radiator setup—and once installed, it’s not easy to change. Get it right the first time.


